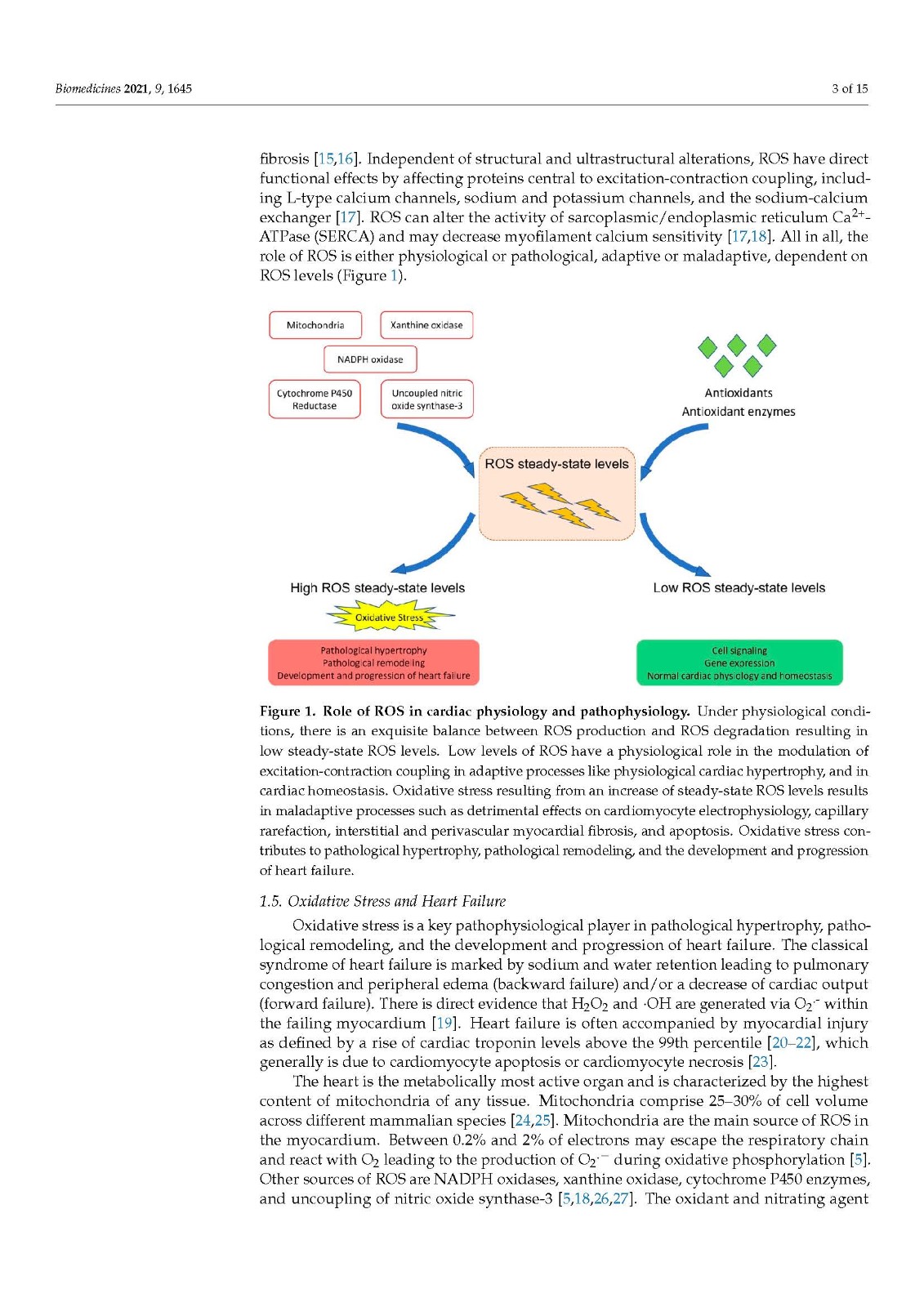
Under physiological circumstances, there is an exquisite balance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and ROS degradation, resulting in low steady-state ROS levels. ROS participate in normal cellular function and in cellular homeostasis. Oxidative stress is the state of a transient or a persistent increase of steady-state ROS levels leading to disturbed signaling pathways and oxidative modification of cellular constituents. It is a key pathophysiological player in pathological hypertrophy, pathological remodeling, and the development and progression of heart failure. The heart is the metabolically most active organ and is characterized by the highest content of mitochondria of any tissue. Mitochondria are the main source of ROS in the myocardium. The causal role of oxidative stress in heart failure is highlighted by gene transfer studies of three primary antioxidant enzymes, thioredoxin, and heme oxygenase-1, and is further supported by gene therapy studies directed at correcting oxidative stress linked to metabolic risk factors. Moreover, gene transfer studies have demonstrated that redox-sensitive microRNAs constitute potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of heart failure. In conclusion, gene therapy studies have provided strong corroborative evidence for a key role of oxidative stress in pathological remodeling and in the development of heart failure.

在生理环境下,活性氧 (ROS) 的产生和 ROS 降解之间存在微妙的平衡,导致稳态 ROS 水平较低。ROS 参与正常的细胞功能和细胞稳态。氧化应激是稳态 ROS 水平短暂或持续增加的状态,导致信号通路紊乱和细胞成分的氧化修饰。它是病理性肥大、病理性重塑以及心力衰竭的发展和进展的关键病理生理参与者。心脏是代谢最活跃的器官,其特征是所有组织中线粒体含量最高。线粒体是心肌中 ROS 的主要来源。三种主要抗氧化酶硫氧还蛋白和血红素加氧酶-1 的基因转移研究强调了氧化应激在心力衰竭中的因果作用,并得到了旨在纠正与代谢风险因素相关的氧化应激的基因治疗研究的进一步支持。此外,基因转移研究表明,氧化还原敏感的 microRNA 是治疗心力衰竭的潜在治疗靶点。总之,基因治疗研究为氧化应激在病理重塑和心力衰竭发展中的关键作用提供了强有力的佐证。基因转移研究表明,氧化还原敏感的 microRNA 是治疗心力衰竭的潜在治疗靶点。总之,基因治疗研究为氧化应激在病理重塑和心力衰竭发展中的关键作用提供了强有力的佐证。基因转移研究表明,氧化还原敏感的 microRNA 是治疗心力衰竭的潜在治疗靶点。总之,基因治疗研究为氧化应激在病理重塑和心力衰竭发展中的关键作用提供了强有力的佐证。
Gene transfer studies have provided strong corroborative evidence for a key role of oxidative stress in pathological cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling and in the development of heart failure. Since the heart is the metabolically most active organ and is characterized by the highest content of mitochondria of any tissue, this organ is very susceptible and vulnerable to oxidative stress. Oxidative stress not only causes protein oxidation, lipid peroxidation, and DNA damage but also oxidative changes of microRNAs [5,11]. The key pathogenetic role of oxidative changes of microRNAs has been unequivocally demonstrated [11].
Furthermore, the cellular levels of redox-sensitive microRNAs are altered in response to oxidative stress, and increasing evidence indicates that these redox-sensitive microRNAs constitute potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of heart failure [105,121,122,123]. The causal role of oxidative stress in heart failure is also supported by gene transfer studies of the three primary antioxidant enzymes (SODs, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase), of thioredoxin, and of heme oxygenase-1. Finally, multiple gene transfer prevention and intervention studies have demonstrated that gene therapy directed at the correction of metabolic risk factors resulted in a marked reduction of systemic oxidative stress and oxidative stress in the myocardium [63,64]. This correction of metabolic risk factors also resulted in improved cardiac function and prevention or reversal of pathological remodeling and heart failure [63,64]. The broad robustness of the strong link between reduction of oxidative stress and prevention and treatment of heart failure suggests that reduction of oxidative stress is an important mediator of the observed effects of metabolic gene therapy on cardiac structure and function.
Heart failure is the cardiovascular epidemic of this century and has a rather dismal prognosis [124]. The development of gene transfer strategies that result in an improved cellular redox state remains an important research area in the generation of new treatments for heart failure.
Author Contributions
B.D.G. conceived the present review. B.D.G. and M.M. did the research, wrote the manuscript, and drew the figures. The intellectual content of the final version of the manuscript was checked by both authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.

细胞转瓶2L
基因转移研究为氧化应激在病理性心脏肥大和重塑以及心力衰竭发展中的关键作用提供了强有力的佐证。由于心脏是代谢最活跃的器官,其特征是任何组织中线粒体含量最高,因此该器官非常容易受到氧化应激的影响。氧化应激不仅会导致蛋白质氧化、脂质过氧化和 DNA 损伤,还会导致 microRNA 的氧化变化。microRNA 氧化变化的关键致病作用已得到明确证明。
此外,氧化还原敏感 microRNA 的细胞水平会因氧化应激而发生改变,越来越多的证据表明这些氧化还原敏感 microRNA 是治疗心力衰竭的潜在治疗靶点。三种主要抗氧化酶(SOD、过氧化氢酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶)、硫氧还蛋白和血红素加氧酶-1 的基因转移研究也支持氧化应激在心力衰竭中的因果作用。最后,多项基因转移预防和干预研究表明,针对代谢危险因素纠正的基因治疗可显着减少心肌中的全身氧化应激和氧化应激。这种代谢危险因素的纠正还导致心脏功能的改善以及病理重塑和心力衰竭的预防或逆转。减少氧化应激与预防和治疗心力衰竭之间的密切联系的广泛稳健性表明,减少氧化应激是观察到的代谢基因治疗对心脏结构和功能的影响的重要介质。
心力衰竭是本世纪的心血管流行病,预后相当差。导致细胞氧化还原状态改善的基因转移策略的开发仍然是产生心力衰竭新疗法的重要研究领域。













来源: MDPI https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/9/11/1645/htm
关键词:gene therapy; gene transfer; heart failure; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; cardiac hypertrophy; cardiac remodeling; microRNA
基因治疗;基因转移;心力衰竭;氧化应激;活性氧;心脏肥大;心脏重塑;微小RNA
上一篇: PETG材料在血清瓶中的应用
下一篇: 细胞工厂内出现细菌污染怎么办